Policies are important frameworks that establish the priority actions and allocation of resources at different government levels. Decisions established through policies in many different sectors can have a profound influence on the health of communities. Click the expandable menu below for articles about the policies and policy considerations for rural Alberta health care.
The Canada Health Act - A Vision for Universal Health Care
Medicare (French: assurance-maladie) is a common name for Canada’s publicly-funded, single-payer health care system. In 1962, Saskatchewan was the first province to introduce a universal, provincial medical insurance plan to provide physician services to all residents. In 1966, the federal government passed the Medical Care Act, and within six years, all the provinces and territories had universal physician services insurance plans. This is what is now called universal health coverage.
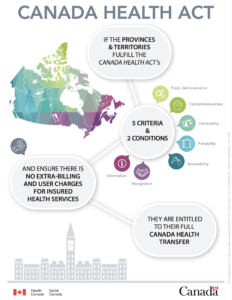
After many reforms, the Canada Health Act (CHA) was passed in 1984. It is the federal law that sets out publicly funded health care insurance for all Canadians. The CHA lays out the vision for Canadian health-care policy:
to protect, promote and restore the physical and mental well-being of residents of Canada and to facilitate reasonable access to health services without financial or other barriers.
This means that when Canadians use public health services, the cost are covered through provincial health insurance plans. Each province is responsible for planning and operating a public health-care system that covers basic health care. The provinces receive funds from the federal government to do this. They must meet the criteria and conditions of the CHA to receive the full federal cash contribution for provincial health-care services.
Universal health coverage is the hallmark of Canada’s health-care system and it is essential to create fair access to care for all Canadians.